
Tableau and its Uses
Tableau is a data visualization tool. This software can simplify raw data into an accessible dashboard format that incorporates visual depictions of raw data, which can then be understood by various professionals working within a company.
Tableau provides features for real-time analysis, data blending, and collaboration capabilities. It allows Data Analysts to manipulate live datasets and devote their efforts more to analysis rather than data wrangling. Because Tableau doesn’t require programming or technical skills, it’s an accessible tool for data analytics.
- Tableau can bring together various data sources into a single point of truth. This provides one central source that’s useful for all types of business reporting.
- Tableau’s automated data reshaper tool can transform any data into the necessary format by splitting fields or eliminating headers or white space.
- Tableau’s automated reporting feature allows you to easily create a report, then set it to focus on a specific dataset so that the data will automatically refresh without requiring any coding knowledge.
- This tool’s visualization capabilities present information clearly, effectively, and engagingly.
Benefits of Developing Tableau for Your Business
Data Visualization
Tableau enables businesses to create visually compelling and interactive dashboards, making it easier to understand and analyze complex data.
Quick Insights
With its user-friendly interface, Tableau allows for rapid data exploration and analysis, helping businesses gain valuable insights promptly.
Increased Efficiency
Tableau automates data analysis and reporting, enhancing operational efficiency by minimizing time and effort in report generation.

Real-time Analytics
Businesses can leverage Tableau for real-time data analytics, enabling timely responses to market changes and emerging trends.
Cost Savings
By streamlining data analysis and reducing the dependence on IT for reporting, Tableau can contribute to cost savings in terms of both time and resources.
Mobile Accessibility
Tableau supports mobile devices, allowing users to access critical business insights anytime, anywhere, fostering a more flexible and agile work environment.
Why Use Tableau
Tableau knowledge is useful in a range of professions and industries. This tool is used by small and large organizations for analyzing and visualizing data and communicating data-related insights and findings. The following sections will briefly explore some of the industries and professions that use Tableau.
- Tableau is a powerful tool that allows professionals working with data to efficiently analyze, visualize, and share their findings.
- Tableau is an in-demand skill in both small and large organizations. It’s also valuable across industries and professional focuses since it can highlight important insights into performance trends.
- Some of the most common professions that use Tableau are Data Analysts, Business Analysts, Accountants, and Financial Analysts.
Our Knowledge Discovery Process
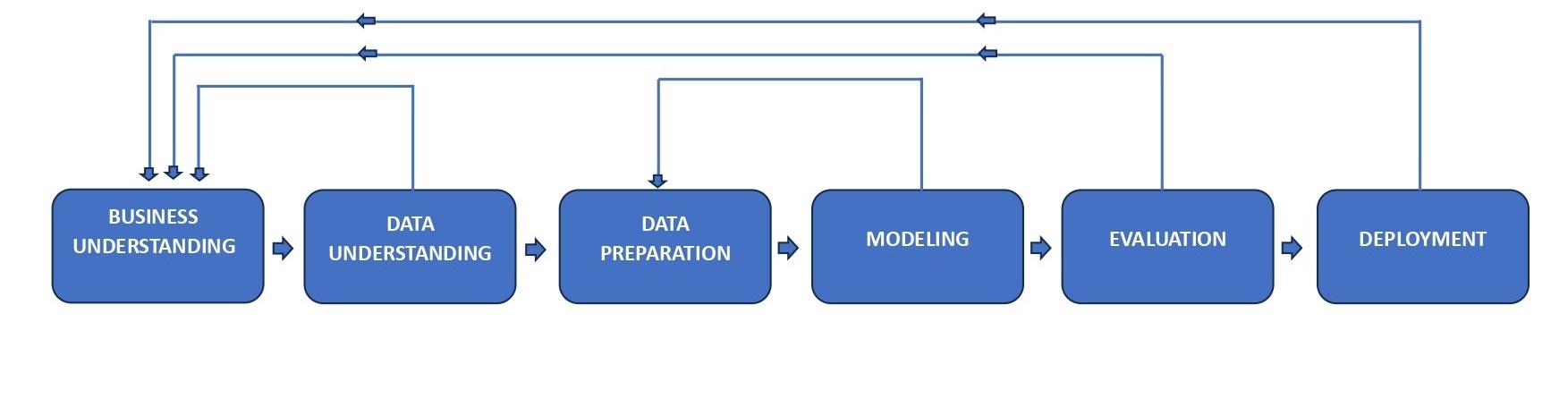
Our Major Tableau Development Services Include
Tableau Consulting
Assisting clients in implementing Tableau solutions, optimizing their data visualization strategies, and integrating Tableau with existing workflows.
Data Visualization & Dashboard Development
Designing interactive dashboards tailored to client needs, enabling them to understand their data and make informed decisions.
Data Integration & Preparation
Helping clients aggregate, clean, and prepare data from various sources for effective Tableau use.
Custom Analytics Solutions
Developing predictive analytics, KPI tracking, and performance dashboards using Tableau.
Performance Optimization
Analyzing and optimizing Tableau dashboards for better performance with large datasets.
Advanced Analytics Integration
Integrating Tableau with Python, R, or machine learning tools for enhanced analysis.
Ongoing Support & Managed Services
Providing ongoing support, updates, and management for Tableau environments.
Tableau Deployment & Support
Assisting in deploying Tableau Server/Online and ensuring smooth support.
Data Analytics
Every day, approximately 2.5 quintillion bytes of data is made. This amount continues to grow as more companies expand their online presence and incorporate technological advances. However, this huge volume of data isn’t actionable until the data can be analyzed. This is where a Data Analyst comes in. Data analytics is a process by which raw data is interpreted, and conclusions are reached about the information contained within them. These insights are then used by stakeholders and decision-makers within an organization to make more informed choices about running the business. The term “data analytics'' describes the different techniques used to analyze unprocessed data to uncover important insights. This process involves a number of steps, such as collecting and organizing data, running statistical analyses, and offering predictions about what may unfold so the organization can select its next steps. Data analytics has a range of real-world applications across professions where data is collected. In addition to working with programming languages like Python and SQL, as well as spreadsheet apps like Excel, Data Analysts also commonly work with Tableau so the data results they find can be visualized. By creating interactive, engaging visual depictions like histograms and pie charts, Data Analysts can tell a data-driven story that can be understood by individuals working at all levels of an organization. These visualizations can also be shared with any relevant stakeholders.
Business Analytics
Business analytics is another profession where Tableau skills are needed. This field is a subset of business intelligence. Business Analysts work with various tools like data mining, statistical analysis, and predictive analysis to analyze data and collect meaningful insights. They also search for any issues that may appear in the data that would require immediate attention. These findings are then visualized using Tableau or a similar problem so they can be shared with others within the organization and used to make better business decisions. Every customer transaction or engagement that takes place in cyberspace leaves a trail of information behind, information that can be profitable if you know what to do with it. Information such as this offers objective facts about customers’ interests, shopping patterns, and purchases. Business Analysts work with these numbers to ensure their organization can profit from this information. Tableau is the most widely used business intelligence platform currently available. This visualization tool helps Business Analysts navigate and manage data, as well as locate insights within the information. Because of how much data continues to be created in the business sector, business analytics is an in-demand field.
Accounting
Accountants are tasked with handling an organization’s bookkeeping and financial documents, like balance sheets and profit statements. They also perform audits on the organization’s books and create reports for tax purposes. Accountants must be extremely detail-oriented and organized since they work with a vast amount of sensitive information. Not only do Accountants need to keep accurate and comprehensive records, but they also interpret financial records. With the help of the data analytics process, Accountants can more easily and quickly perform routine tasks, such as analyzing data and identifying patterns or concerning outliers. Although there are many kinds of accounting, the field is typically broken into three primary career paths with their own professional focus: Management Accountants, Public Accountants, and Government Accountants. Most Accountants work for individual clients or are hired by a larger organization. Many accountants work with Microsoft Excel to perform data-related tasks. Tableau is growing increasingly popular among these professionals as well. Tableau is often preferred to Excel because of how easy it is to create charts that highlight more aspects or “views” of the data, rather than the basic tables Excel can generate. Although Tableau isn’t necessarily a replacement for spreadsheet apps like Excel, many Accountants use these tools together to perform faster data analytics and to share their results. Excel is useful for tasks like ad hoc data management, basic computational solutions and calculations, and small-scale scenario analysis. Tableau, on the other hand, can join and merge data and is able to handle huge datasets. Its visual interface can analyze large amounts of complicated data and create interactive dashboards to convey data findings.
Financial Analytics
Another industry that relies heavily on Tableau for data analytics and visualization is financial analytics. Like Business Analysts and Data Analysts, Financial Analysts are involved with gathering and organizing data. They also compare historical results and generate reports designed to project possible outcomes for their organization. Financial Analysts create reports, budget models, Excel models, and interactive data visualizations to share their results. Although the daily tasks of Financial Analysts depend on their industry focus and employer, these professionals typically perform industry-specific trends in economics, finance, and business, and review the organization’s financial statements. They design models for various investors and provide recommendations for single investments as well as investment collections. Financial Analysts also evaluate the performance of stocks and bonds and stay current on new technological developments and current market conditions. Those involved with financial analytics must be literate in financial jargon and know acronyms like ROA, ROE, and EPS. They also work regularly with statistics, databases, programming languages and other data analytics tools like Tableau so their data findings can be clearly expressed and shared with relevant stakeholders.